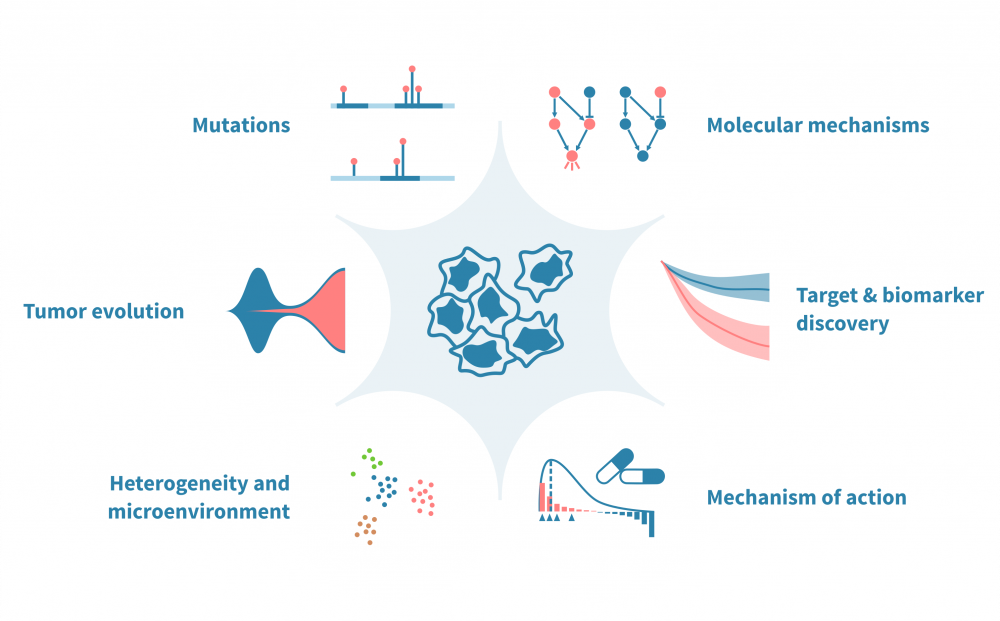
Understand cancer, develop new drugs and personalize treatment with Genevia Technologies.
Our history in cancer bioinformatics is long: we have had the privilege to work with biologists seeking for a deeper understanding of cancer, companies developing new treatments to cancer, as well as oncologists wishing to optimize therapies to individual patients.